Linux的进程存在多种状态,如TASK_RUNNING的运行态、EXIT_DEAD的停止态和 TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE的接收信号的等待状态等等(可在include/linux/sched.h中查看)。其中有一种状态等待为 TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE,称为D状态,该种状态下进程不接收信号,只能通过wake_up唤醒。 处于这种状态的情况有很多,例如mutex锁就可能会设置进程于该状态,有时候进程在等待某种IO资源就绪时 (wait_event机制)会设置进程进入该状态。一般情况下,进程处于该状态的时间不会太久,但若IO设备出现故障 或者出现进程死锁等情况,进程就可能长期处于该状态而无法再返回到TASK_RUNNING态。因此,内核为了便于发现 这类情况设计出了hung task机制专门用于检测长期处于D状态的进程并发出告警。 本文分析内核hung task机制的源码并给出一个示例演示。
一、hung task机制分析
内核在很早的版本中就已经引入了hung task机制, 本文以较新的Linux 4.1.15版本源码为例进行分析,代码量并不多,源代码文件为kernel/hung_task.c。
首先给出整体流程框图和设计思想:
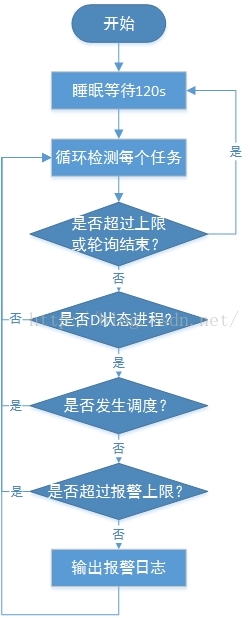
图 D状态死锁流程图
其核心思想为创建一个内核监测进程循环监测处于D状态的每一个进程(任务), 统计它们在两次检测之间的调度次数,如果发现有任务在两次监测之间没有发生任何的调度则可判断该进程一直处于D状态, 很有可能已经死锁,因此触发报警日志打印,输出进程的基本信息,栈回溯以及寄存器保存信息以供内核开发人员定位。
下面详细分析实现方式:
static int __init hung_task_init(void)
{
atomic_notifier_chain_register(&panic_notifier_list, &panic_block);
watchdog_task = kthread_run(watchdog, NULL, "khungtaskd");
return 0;
}
subsys_initcall(hung_task_init);
首先,若在内核配置中启用了该机制,在内核的subsys初始化阶段就会调用 hung_task_init()函数启用功能,首先向内核的panic_notifier_list通知链注册回调:
static struct notifier_block panic_block = {
.notifier_call = hung_task_panic,
};
在内核触发panic时就会调用该hung_task_panic()函数,这个函数的作用稍后再看。 继续往下初始化,调用kthread_run()函数创建了一个名为khungtaskd的线程,执行watchdog()函数, 立即尝试调度执行。该线程就是专用于检测D状态死锁进程的后台内核线程。
/*
* kthread which checks for tasks stuck in D state
*/
static int watchdog(void *dummy)
{
set_user_nice(current, 0);
for ( ; ; ) {
unsigned long timeout = sysctl_hung_task_timeout_secs;
while (schedule_timeout_interruptible(timeout_jiffies(timeout)))
timeout = sysctl_hung_task_timeout_secs;
if (atomic_xchg(&reset_hung_task, 0))
continue;
check_hung_uninterruptible_tasks(timeout);
}
return 0;
}
本进程首先设置优先级为0,即一般优先级,不影响其他进程。然后进入主循环 (每隔timeout时间执行一次),首先让进程睡眠,设置的睡眠时间为CONFIG_DEFAULT_HUNG_TASK_TIMEOUT, 可以通过内核配置选项修改,默认值为120s,睡眠结束被唤醒后判断原子变量标识reset_hung_task, 若被置位则跳过本轮监测,同时会清除该标识。该标识通过reset_hung_task_detector()函数设置 (目前内核中尚无其他程序使用该接口):
void reset_hung_task_detector(void)
{
atomic_set(&reset_hung_task, 1);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(reset_hung_task_detector);
接下来循环的最后即为监测函数check_hung_uninterruptible_tasks(),函数入参为监测超时时间。
/*
* Check whether a TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE does not get woken up for
* a really long time (120 seconds). If that happens, print out
* a warning.
*/
static void check_hung_uninterruptible_tasks(unsigned long timeout)
{
int max_count = sysctl_hung_task_check_count;
int batch_count = HUNG_TASK_BATCHING;
struct task_struct *g, *t;
/*
* If the system crashed already then all bets are off,
* do not report extra hung tasks:
*/
if (test_taint(TAINT_DIE) || did_panic)
return;
rcu_read_lock();
for_each_process_thread(g, t) {
if (!max_count--)
goto unlock;
if (!--batch_count) {
batch_count = HUNG_TASK_BATCHING;
if (!rcu_lock_break(g, t))
goto unlock;
}
/* use "==" to skip the TASK_KILLABLE tasks waiting on NFS */
if (t->state == TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE)
check_hung_task(t, timeout);
}
unlock:
rcu_read_unlock();
}
首先检测内核是否已经DIE了或者已经panic了,如果是则表明内核已经crash了, 无需再进行监测了,直接返回即可。注意这里的did_panic标识在前文中的panic通知链回调函数中hung_task_panic()置位:
static int
hung_task_panic(struct notifier_block *this, unsigned long event, void *ptr)
{
did_panic = 1;
return NOTIFY_DONE;
}
接下去若尚无触发内核crash,则进入监测流程并逐一检测内核中的所有进程(任务task), 该过程在RCU加锁的状态下进行,因此为了避免在进程较多的情况下加锁时间过长,这里设置了一个batch_count, 一次最多检测HUNG_TASK_BATCHING个进程。于此同时用户也可以设定最大的检测个数max_count=sysctl_hung_task_check_count, 默认值为最大PID个数PID_MAX_LIMIT(通过sysctl命令设置)。
函数调用for_each_process_thread()函数轮询内核中的所有进程(任务task), 仅对状态处于TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE状态的进程进行超时判断,调用check_hung_task()函数, 入参为task_struct结构和超时时间(120s):
static void check_hung_task(struct task_struct *t, unsigned long timeout)
{
unsigned long switch_count = t->nvcsw + t->nivcsw;
/*
* Ensure the task is not frozen.
* Also, skip vfork and any other user process that freezer should skip.
*/
if (unlikely(t->flags & (PF_FROZEN | PF_FREEZER_SKIP)))
return;
/*
* When a freshly created task is scheduled once, changes its state to
* TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE without having ever been switched out once, it
* musn't be checked.
*/
if (unlikely(!switch_count))
return;
if (switch_count != t->last_switch_count) {
t->last_switch_count = switch_count;
return;
}
trace_sched_process_hang(t);
if (!sysctl_hung_task_warnings)
return;
if (sysctl_hung_task_warnings > 0)
sysctl_hung_task_warnings--;
首先通过t->nvcsw和t->nivcsw的计数累加表示进程从创建开始至今的调度次数总和, 其中t->nvcsw表示进程主动放弃CPU的次数,t->nivcsw表示被强制抢占的次数。随后函数判断几个标识:
- 如果进程被frozen了那就跳过检测;
- 调度次数为0的不检测。
接下来判断从上一次检测时保存的进程调度次数和本次是否相同, 若不相同则表明这轮timeout(120s)时间内进程发生了调度,则更新该调度值返回, 否则则表明该进程已经有timeout(120s)时间没有得到调度了,一直处于D状态。 接下来的trace_sched_process_hang()暂不清楚作用,然后判断sysctl_hung_task_warnings标识, 它表示需要触发报警的次数,用户也可以通过sysctl命令配置,默认值为10,即若当前检测的进程一直处于D状态, 默认情况下此处每2分钟发出一次告警,一共发出10次,之后不再发出告警。下面来看告警代码:
/*
* Ok, the task did not get scheduled for more than 2 minutes,
* complain:
*/
pr_err("INFO: task %s:%d blocked for more than %ld seconds.\n",
t->comm, t->pid, timeout);
pr_err(" %s %s %.*s\n",
print_tainted(), init_utsname()->release,
(int)strcspn(init_utsname()->version, " "),
init_utsname()->version);
pr_err("\"echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/hung_task_timeout_secs\""
" disables this message.\n");
sched_show_task(t);
debug_show_held_locks(t);
touch_nmi_watchdog();
这里会在控制台和日志中打印死锁任务的名称、PID号、超时时间、内核tainted信息、 sysinfo、内核栈barktrace以及寄存器信息等。如果开启了debug lock则打印锁占用的情况,并touch nmi_watchdog 以防止nmi_watchdog超时(对于我的ARM环境无需考虑nmi_watchdog)。
if (sysctl_hung_task_panic) {
trigger_all_cpu_backtrace();
panic("hung_task: blocked tasks");
}
最后如果设置了sysctl_hung_task_panic标识则直接触发panic (该值可通过内核配置文件配置也可以通过sysctl设置)。
二、示例演示
演示环境:树莓派b(Linux 4.1.15)
首先确认内核配置选项以确认开启hung stak机制
Kernel hacking --->
Debug Lockups and Hangs --->
[*] Detect Hung Tasks
(120) Default timeout for hung task detection (in seconds)
编写测试程序
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
DEFINE_MUTEX(dlock);
static int __init dlock_init(void)
{
mutex_lock(&dlock);
mutex_lock(&dlock);
return 0;
}
static void __exit dlock_exit(void)
{
return;
}
module_init(dlock_init);
module_exit(dlock_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
本示例程序定义了一个mutex锁,然后在模块的init函数中重复加锁,人为造成死锁现象 (mutex_lock()函数会调用__mutex_lock_slowpath()将进程设置为TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE状态), 进程进入D状态后是无法退出的。可以通过ps命令来查看:
root@apple:~# busybox ps
PID USER TIME COMMAND
……
521 root 0:00 insmod dlock.ko
……
然后查看该进程的状态,可见已经进入了D状态
root@apple:~# cat /proc/521/status
Name: insmod
State: D (disk sleep)
Tgid: 521
Ngid: 0
Pid: 521
至此在等待两分钟后调试串口就会输出以下信息,可见每两分钟就会输出一次:
[ 360.625466] INFO: task insmod:521 blocked for more than 120 seconds.
[ 360.631878] Tainted: G O 4.1.15 #5
[ 360.637042] “echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/hung_task_timeout_secs” disables this message.
[ 360.644986] [
] (__schedule) from [ ] (schedule+0x40/0xa4) [ 360.652129] [
] (schedule) from [ ] (schedule_preempt_disabled+0x18/0x1c) [ 360.660570] [
] (schedule_preempt_disabled) from [ ] (__mutex_lock_slowpath+0x6c/0xe4) [ 360.670142] [
] (__mutex_lock_slowpath) from [ ] (mutex_lock+0x44/0x48) [ 360.678432] [
] (mutex_lock) from [ ] (dlock_init+0x20/0x2c [dlock]) [ 360.686480] [
] (dlock_init [dlock]) from [ ] (do_one_initcall+0x90/0x1e8) [ 360.694976] [
] (do_one_initcall) from [ ] (do_init_module+0x6c/0x1c0) [ 360.703170] [
] (do_init_module) from [ ] (load_module+0x1690/0x1d34) [ 360.711284] [
] (load_module) from [ ] (SyS_init_module+0xdc/0x130) [ 360.719239] [
] (SyS_init_module) from [ ] (ret_fast_syscall+0x0/0x54) [ 480.725351] INFO: task insmod:521 blocked for more than 120 seconds.
[ 480.731759] Tainted: G O 4.1.15 #5
[ 480.736917] “echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/hung_task_timeout_secs” disables this message.
[ 480.744842] [
] (__schedule) from [ ] (schedule+0x40/0xa4) [ 480.752029] [
] (schedule) from [ ] (schedule_preempt_disabled+0x18/0x1c) [ 480.760479] [
] (schedule_preempt_disabled) from [ ] (__mutex_lock_slowpath+0x6c/0xe4) [ 480.770066] [
] (__mutex_lock_slowpath) from [ ] (mutex_lock+0x44/0x48) [ 480.778363] [
] (mutex_lock) from [ ] (dlock_init+0x20/0x2c [dlock]) [ 480.786402] [
] (dlock_init [dlock]) from [ ] (do_one_initcall+0x90/0x1e8) [ 480.794897] [
] (do_one_initcall) from [ ] (do_init_module+0x6c/0x1c0) [ 480.803085] [
] (do_init_module) from [ ] (load_module+0x1690/0x1d34) [ 480.811188] [
] (load_module) from [ ] (SyS_init_module+0xdc/0x130) [ 480.819113] [
] (SyS_init_module) from [ ] (ret_fast_syscall+0x0/0x54) [ 600.825353] INFO: task insmod:521 blocked for more than 120 seconds.
[ 600.831759] Tainted: G O 4.1.15 #5
[ 600.836916] “echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/hung_task_timeout_secs” disables this message.
[ 600.844865] [
] (__schedule) from [ ] (schedule+0x40/0xa4) [ 600.852005] [
] (schedule) from [ ] (schedule_preempt_disabled+0x18/0x1c) [ 600.860445] [
] (schedule_preempt_disabled) from [ ] (__mutex_lock_slowpath+0x6c/0xe4) [ 600.870014] [
] (__mutex_lock_slowpath) from [ ] (mutex_lock+0x44/0x48) [ 600.878303] [
] (mutex_lock) from [ ] (dlock_init+0x20/0x2c [dlock]) [ 600.886339] [
] (dlock_init [dlock]) from [ ] (do_one_initcall+0x90/0x1e8) [ 600.894835] [
] (do_one_initcall) from [ ] (do_init_module+0x6c/0x1c0) [ 600.903023] [
] (do_init_module) from [ ] (load_module+0x1690/0x1d34) [ 600.911133] [
] (load_module) from [ ] (SyS_init_module+0xdc/0x130) [ 600.919059] [
] (SyS_init_module) from [ ] (ret_fast_syscall+0x0/0x54)
三、总结
D状态死锁一般在驱动开发的过程中比较常见,且不太容易定位,内核提供这种hung task机制, 开发人员只需要将这些输出的定位信息抓取并保留下来就可以快速的进行定位。
文档信息
--------------
* 版权声明:自由转载-非商用
* 转载: [My Linux Journey]