前一篇博文介绍了内核监测D状态死锁的hung task机制,本文介绍另一种死锁状态的 监测手段——R状态死锁监测。R状态死锁指的是某一任务一直处于TASK_RUNNING态且一直占用着CPU, 从而导致其他进程得不到调度而饿死的情况。一般情况下,R状态死锁较可能是由于程序出现死循环导致的, 可以出现在内核态的进程上下文中(内核配置为非抢占式,soft lockup),也可以出现在中断上下文中的 中断处理程序中(hard lockup)。异常的程序一直运行,CPU无法调度到其他的任务运行,对于单CPU的设备, 则直接的表现就是“死机”。这种死锁现象较难定位,内核也同样提供了一种检测手段来检测这种死锁并向用户发出 告警——LOCKUP_DETECTOR,它可支持监测进程上下文和中断上下文中的R状态死锁(SOFTLOCKUP_DETECTOR和HARDLOCKUP_DETECTOR), 由于HARDLOCKUP_DETECTOR需要nmi中断的支持且目前的arm32环境并不支持,本文仅分析其中SOFTLOCKUP_DETECTOR中的 原理及实现方式,并给出一个示例。
一、lockup detector机制分析
lockup detector机制在内核代码的kernel/watchdog.c中实现, 本文以Linux 4.1.15版本源码为例进行分析。首先了解其背后的设计原理:利用进程上下文、中断、 nmi中断的不同优先级实现死锁监测。它们3者的优先级关系为“进程上下文 < 中断 < nmi中断”, 其中进程上下文优先级最低,可通过中断来进行监测进程的运行状态,nmi中断的优先级最高, 它是一种不可屏蔽的中断,在中断上下文中发生死锁时,nmi中断处理也可正常进入,因此可用来监测中断中的死锁。 不过可惜的是目前绝大多数的arm32芯片都不支持nmi中断,也包括我手中树莓派的bcm2835芯片。 从程序的命名中就可以看出,该程序其实实现了一种软看门狗的功能,下面给出整体的软件流程框图:
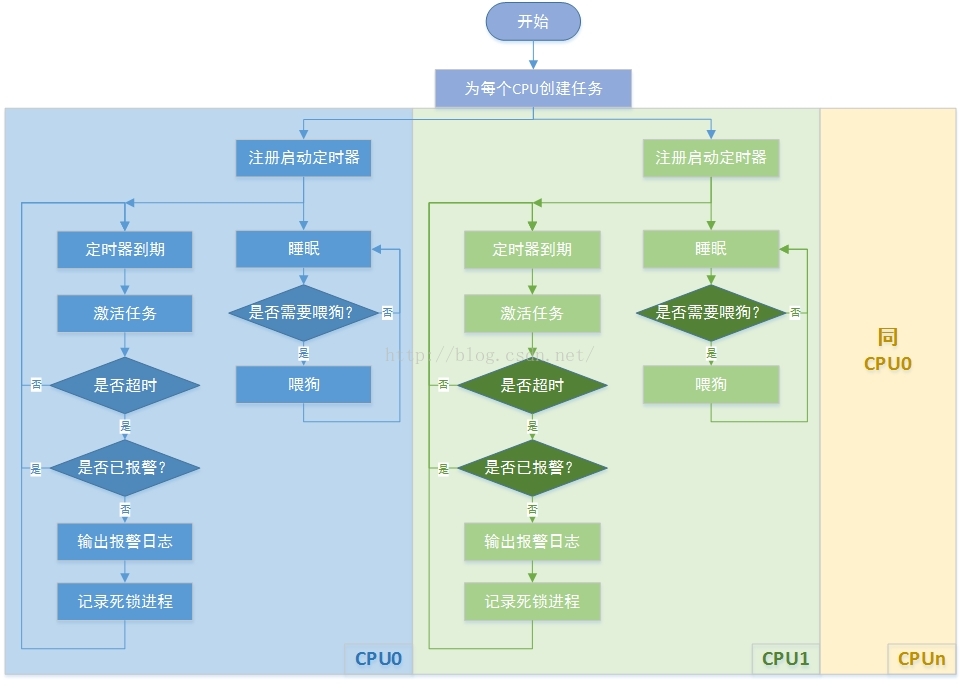
图 D状态死锁流程图
该程序为每个cpu创建了一个进程和一个高精度定时器,其中进程用来喂狗, 定时器用来唤醒喂狗进程和检测是否存在死锁进程,在检测到死锁进程后就触发报警, 接下来详细分析源代码:
void __init lockup_detector_init(void)
{
set_sample_period();
if (watchdog_enabled)
watchdog_enable_all_cpus();
}
首先入口函数lockup_detector_init(),该函数会在内核启动流程中按如下路径调用: start_kernel() –> rest_init() –> kernel_init()(启内核线程)–> kernel_init_freeable() –> lockup_detector_init()。该函数首先计算高精度定时器的到期时间(即喂狗时间),该值为监测超时时间值的1/5, 默认为4s(20s/5),然后判断开关标识来确定是否启用监测机制,该标识在没有启用hard lockup detect的 情况下默认为SOFT_WATCHDOG_ENABLED,表示开启soft lockup detect。于此同时内核也提供了如下的__setup接口, 可从内核启动参数cmd line中设置值和开关:
static int __init softlockup_panic_setup(char *str)
{
softlockup_panic = simple_strtoul(str, NULL, 0);
return 1;
}
__setup("softlockup_panic=", softlockup_panic_setup);
static int __init nowatchdog_setup(char *str)
{
watchdog_enabled = 0;
return 1;
}
__setup("nowatchdog", nowatchdog_setup);
static int __init nosoftlockup_setup(char *str)
{
watchdog_enabled &= ~SOFT_WATCHDOG_ENABLED;
return 1;
}
__setup("nosoftlockup", nosoftlockup_setup);
此处假定开启soft lockup detect,接下来调用watchdog_enable_all_cpus()函数, 该函数会尝试为每个CPU创建一个喂狗任务(并不会立即启动主函数执行):
static int watchdog_enable_all_cpus(void)
{
int err = 0;
if (!watchdog_running) {
err = smpboot_register_percpu_thread(&watchdog_threads);
if (err)
pr_err("Failed to create watchdog threads, disabled\n");
else
watchdog_running = 1;
} else {
/*
* Enable/disable the lockup detectors or
* change the sample period 'on the fly'.
*/
update_watchdog_all_cpus();
}
return err;
}
该函数首先判断是否已经启动了任务,若没有则调用smpboot_register_percpu_thread()函数来创建任务, 否则则调用update_watchdog_all_cpus()函数来更新定时器的到期时间。首先分析前一个分支,看一下watchdog_threads结构体的实现:
static struct smp_hotplug_thread watchdog_threads = {
.store = &softlockup_watchdog,
.thread_should_run = watchdog_should_run,
.thread_fn = watchdog,
.thread_comm = "watchdog/%u",
.setup = watchdog_enable,
.cleanup = watchdog_cleanup,
.park = watchdog_disable,
.unpark = watchdog_enable,
};
该结构注册了许多的回调函数,先简单了解一下:
- softlockup_watchdog是一个全局的per cpu指针,它用来保存创建任务的进程描述符task_struct结构;
- watchdog_should_run()是任务运行的判断函数,它会判断进程是否需要调用thread_fn指针指向的函数运行;
- watchdog()是任务运行的主函数,该函数实现线程喂狗的动作;
- setup回调函数watchdog_enable会在任务首次启动时调用,该函数会创建高精度定时器,用来激活喂狗任务和监测死锁超时;
- cleanup回调函数用来清除任务,它会关闭定时器;
- 最后的park和unpark回调函数用于暂停运行和恢复运行任务。
- thread_comm是任务名字,cpu0是watchdog/0,cpu1是watchdog/1,
以此类推。下面来简单看一下smpboot_register_percpu_thread()函数是如何为每个cpu创建任务的, 同时又在何处调用上述的那些回调函数的(kernel/smpboot.c):
int smpboot_register_percpu_thread(struct smp_hotplug_thread *plug_thread)
{
unsigned int cpu;
int ret = 0;
get_online_cpus();
mutex_lock(&smpboot_threads_lock);
for_each_online_cpu(cpu) {
ret = __smpboot_create_thread(plug_thread, cpu);
if (ret) {
smpboot_destroy_threads(plug_thread);
goto out;
}
smpboot_unpark_thread(plug_thread, cpu);
}
list_add(&plug_thread->list, &hotplug_threads);
out:
mutex_unlock(&smpboot_threads_lock);
put_online_cpus();
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(smpboot_register_percpu_thread);
函数遍历所有的online cpu然后为其创建指定的任务, 然后将他们添加到hotplug_threads中去(该链表是用来遍历用的);
static int
__smpboot_create_thread(struct smp_hotplug_thread *ht, unsigned int cpu)
{
struct task_struct *tsk = *per_cpu_ptr(ht->store, cpu);
......
tsk = kthread_create_on_cpu(smpboot_thread_fn, td, cpu,
ht->thread_comm);
......
return 0;
}
可以看出,为每个cpu创建的任务并不是直接调用前文中注册的thread_fn()回调函数, 而是调用了smpboot_thread_fn()函数,该函数会维护任务运行的几个状态,视状态的不同调用不同的注册回调处理函数:
static int smpboot_thread_fn(void *data)
{
struct smpboot_thread_data *td = data;
struct smp_hotplug_thread *ht = td->ht;
while (1) {
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
preempt_disable();
if (kthread_should_stop()) {
__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
preempt_enable();
if (ht->cleanup)
ht->cleanup(td->cpu, cpu_online(td->cpu));
kfree(td);
return 0;
}
if (kthread_should_park()) {
__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
preempt_enable();
if (ht->park && td->status == HP_THREAD_ACTIVE) {
BUG_ON(td->cpu != smp_processor_id());
ht->park(td->cpu);
td->status = HP_THREAD_PARKED;
}
kthread_parkme();
/* We might have been woken for stop */
continue;
}
BUG_ON(td->cpu != smp_processor_id());
/* Check for state change setup */
switch (td->status) {
case HP_THREAD_NONE:
__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
preempt_enable();
if (ht->setup)
ht->setup(td->cpu);
td->status = HP_THREAD_ACTIVE;
continue;
case HP_THREAD_PARKED:
__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
preempt_enable();
if (ht->unpark)
ht->unpark(td->cpu);
td->status = HP_THREAD_ACTIVE;
continue;
}
if (!ht->thread_should_run(td->cpu)) {
preempt_enable_no_resched();
schedule();
} else {
__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
preempt_enable();
ht->thread_fn(td->cpu);
}
}
}
这个函数是一个大循环,在每次循环中都会首先依次判断是否需要停止本任务、 是否需要park本任务,如果是则进行相应的处理,可以看到这里就会调用前文中注册的cleanup()和park()回调函数; 如果不需要stop和park则接下来按照状态机处理,对于初次运行的任务,这里会调用setup()回调进行相应的初始化动作; 最后对于在正常运行中的最一般情况下,会调用thread_should_run回调判断是否需要调用注册主函数, 视判断的返回值情况调用thread_fn()函数。下面来看前文中注册的setup回调watchdog_enable():
static void watchdog_enable(unsigned int cpu)
{
struct hrtimer *hrtimer = raw_cpu_ptr(&watchdog_hrtimer);
/* kick off the timer for the hardlockup detector */
hrtimer_init(hrtimer, CLOCK_MONOTONIC, HRTIMER_MODE_REL);
hrtimer->function = watchdog_timer_fn;
/* Enable the perf event */
watchdog_nmi_enable(cpu);
/* done here because hrtimer_start can only pin to smp_processor_id() */
hrtimer_start(hrtimer, ns_to_ktime(sample_period),
HRTIMER_MODE_REL_PINNED);
/* initialize timestamp */
watchdog_set_prio(SCHED_FIFO, MAX_RT_PRIO - 1);
__touch_watchdog();
}
值得注意的是,这个函数是每个online的cpu都会运行的,首先从per cpu变量中获取 本cpu的高精度定时器指针hrtimer并初始化之,注册定时器到期调用函数watchdog_timer_fn(),然后启动定时器, 指定到期时间就是前文中计算的sample_period(4s),最后调整当前进程的调度策略为FIFO实时进程并提高优先级, 这么做是为了保证本喂狗任务能够以较高的优先级运行,以免无法及时喂狗而出现误报的情况。 函数最后调用__touch_watchdog()函数执行首次喂狗动作。
static void __touch_watchdog(void)
{
__this_cpu_write(watchdog_touch_ts, get_timestamp());
}
这里的watchdog_touch_ts也是一个per cpu变量,每个cpu维护自己独有的。 这里将当前系统计时的时钟值(单位ns)以约等于的形式转换的秒单位的值,然后刷新到watchdog_touch_ts中,以此模拟喂狗的动作。 定时器初始化完成后,接下来smpboot_thread_fn()函数就会调用thread_should_run()回调函数watchdog_should_run():
static int watchdog_should_run(unsigned int cpu)
{
return __this_cpu_read(hrtimer_interrupts) !=
__this_cpu_read(soft_lockup_hrtimer_cnt);
}
此处只是比较了两个变量,当这两个变量不相等时才会调用thread_fn()回调, 否则将任务设置为TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE状态然后调度(睡眠)。那这两个变量值合适才会不一样呢? 下面来分析另外一条路,注意前文中的定时器已经启动了,来看一下sample_period时间到期后的调用函数, 这个函数比较长,分段来看:
/* watchdog kicker functions */
static enum hrtimer_restart watchdog_timer_fn(struct hrtimer *hrtimer)
{
unsigned long touch_ts = __this_cpu_read(watchdog_touch_ts);
struct pt_regs *regs = get_irq_regs();
int duration;
int softlockup_all_cpu_backtrace = sysctl_softlockup_all_cpu_backtrace;
/* kick the hardlockup detector */
watchdog_interrupt_count();
/* kick the softlockup detector */
wake_up_process(__this_cpu_read(softlockup_watchdog));
/* .. and repeat */
hrtimer_forward_now(hrtimer, ns_to_ktime(sample_period));
首先获取最后一次的喂狗时间并保存在touch_ts中,然后调用watchdog_interrupt_count() 函数累加hrtimer_interrupts值,显然该值表示的是当前cpu触发定时器中断的次数。
然后尝试唤醒已经睡眠的喂狗线程(注意,由于这里改变了hrtimer_interrupts值, 前文中的watchdog_should_run自然就会返回TRUE了,那么就可以执行注册的主函数了)。 接着本函数继续注册下一次的定时器到期时间。
if (touch_ts == 0) {
if (unlikely(__this_cpu_read(softlockup_touch_sync))) {
/*
* If the time stamp was touched atomically
* make sure the scheduler tick is up to date.
*/
__this_cpu_write(softlockup_touch_sync, false);
sched_clock_tick();
}
/* Clear the guest paused flag on watchdog reset */
kvm_check_and_clear_guest_paused();
__touch_watchdog();
return HRTIMER_RESTART;
}
这个判断在kgdb的调试中会用到,正常情况下不会进入,不做分析,继续往下:
/* check for a softlockup
* This is done by making sure a high priority task is
* being scheduled. The task touches the watchdog to
* indicate it is getting cpu time. If it hasn't then
* this is a good indication some task is hogging the cpu
*/
duration = is_softlockup(touch_ts);
这里调用is_softlockup()函数返回当前时刻是否已经超过了“看门狗”的到期时间:
static int is_softlockup(unsigned long touch_ts)
{
unsigned long now = get_timestamp();
if (watchdog_enabled & SOFT_WATCHDOG_ENABLED) {
/* Warn about unreasonable delays. */
if (time_after(now, touch_ts + get_softlockup_thresh()))
return now - touch_ts;
}
return 0;
}
这里首先判断是否开启了soft lockup detect,是且已经超时的情况下(默认的超时时间是20s)返回超时时间间隔, 否则返回0。下面来看一下超时的情况下会执行哪些处理:
if (unlikely(duration)) {
......
/* only warn once */
if (__this_cpu_read(soft_watchdog_warn) == true) {
/*
* When multiple processes are causing softlockups the
* softlockup detector only warns on the first one
* because the code relies on a full quiet cycle to
* re-arm. The second process prevents the quiet cycle
* and never gets reported. Use task pointers to detect
* this.
*/
if (__this_cpu_read(softlockup_task_ptr_saved) !=
current) {
__this_cpu_write(soft_watchdog_warn, false);
__touch_watchdog();
}
return HRTIMER_RESTART;
}
soft_watchdog_warn标识会在已经出现了一次看门狗超时的情况下置位,此处的用意是对于同一个死锁进程, 内核只做一次报警动作,如果死锁的进程发生了改变,那该标识会重新设置为false,将可以重新触发报警。
if (softlockup_all_cpu_backtrace) {
/* Prevent multiple soft-lockup reports if one cpu is already
* engaged in dumping cpu back traces
*/
if (test_and_set_bit(0, &soft_lockup_nmi_warn)) {
/* Someone else will report us. Let's give up */
__this_cpu_write(soft_watchdog_warn, true);
return HRTIMER_RESTART;
}
}
softlockup_all_cpu_backtrace是一个开关,用来表示是否需要在一个cpu超时时打印所有cpu的backtrace信息, 可以通过sysctrl进行控制。此处的用以是为了避免多个cpu再检测到死锁是同时调用trigger_allbutself_cpu_backtrace 函数打印所有cpu的backtrace信息,因为在同一时刻只需要调用一次就可以了。
pr_emerg("BUG: soft lockup - CPU#%d stuck for %us! [%s:%d]\n",
smp_processor_id(), duration,
current->comm, task_pid_nr(current));
__this_cpu_write(softlockup_task_ptr_saved, current);
print_modules();
print_irqtrace_events(current);
if (regs)
show_regs(regs);
else
dump_stack();
这里就开始依次打印出内核模块信息,中断信息,中断栈信息和backtrace信息,然后记录下了触发死锁的任务描述符task_struct。
if (softlockup_all_cpu_backtrace) {
/* Avoid generating two back traces for current
* given that one is already made above
*/
trigger_allbutself_cpu_backtrace();
clear_bit(0, &soft_lockup_nmi_warn);
/* Barrier to sync with other cpus */
smp_mb__after_atomic();
}
这里同前面相呼应,调用trigger_allbutself_cpu_backtrace()函数打印出了所有cpu的backtrace信息,这个函数是arch架构相关的。
add_taint(TAINT_SOFTLOCKUP, LOCKDEP_STILL_OK);
if (softlockup_panic)
panic("softlockup: hung tasks");
__this_cpu_write(soft_watchdog_warn, true);
最后如果设置了panic标识,则直接触发panic,否则置位了报警标识,后续针对触发本次报警的死锁任务将不再报警。 分析完超时的处理方式,回过头分析一下前文中的喂狗进程是如何运行的。
static void watchdog(unsigned int cpu)
{
__this_cpu_write(soft_lockup_hrtimer_cnt,
__this_cpu_read(hrtimer_interrupts));
__touch_watchdog();
/*
* watchdog_nmi_enable() clears the NMI_WATCHDOG_ENABLED bit in the
* failure path. Check for failures that can occur asynchronously -
* for example, when CPUs are on-lined - and shut down the hardware
* perf event on each CPU accordingly.
*
* The only non-obvious place this bit can be cleared is through
* watchdog_nmi_enable(), so a pr_info() is placed there. Placing a
* pr_info here would be too noisy as it would result in a message
* every few seconds if the hardlockup was disabled but the softlockup
* enabled.
*/
if (!(watchdog_enabled & NMI_WATCHDOG_ENABLED))
watchdog_nmi_disable(cpu);
}
这里首先将hrtimer_interrupts的值付给soft_lockup_hrtimer_cnt, 这样在本次喂狗结束后到下一次定时器到期前,该函数不会投入运行,进程将进入睡眠状态。该函数剩下的就很简单了, 直接调用__touch_watchdog()函数执行喂狗动作。
以上就是进程上下文中的R状态死锁的核心监测代码,该程序还提供了一些可以通过sysctrl 控制启停和超时时间等的接口,比较简单就不分析了。从以上实现可以看出其本质就是利用了hr定时器中断处理 函数周期性的唤醒进程执行软喂狗动作,同时自身则检测软看门狗是否超时。在正常的情况下,当前cpu的定时器中唤醒 的喂狗进程一定是能够得到调度的(视cpu负荷情况可能略有延时),即是不可能超过设定的超时时间的, 但是如果当前cpu中的某一个进程占用cpu时间超过了设定的超时时间(20s), 就会直接导致软看门狗超时并触发一次报警动作,如果这个进程一直不释放cpu(例如while循环), 那么也只会报警一次,反之会重新开启报警功能。
二、示例演示
演示环境:树莓派b(Linux 4.1.15)
首先确认启用内核配置
Kernel hacking --->
Debug Lockups and Hangs --->
[*] Detect Hard and Soft Lockups
[*] Panic (Reboot) On Soft Lockups(可选)
然后确认内核调度策略配置
Kernel Features --->
Preemption Model (Voluntary Kernel Preemption (Desktop))
( ) No Forced Preemption (Server)
(X) Voluntary Kernel Preemption (Desktop)
( ) Preemptible Kernel (Low-Latency Desktop)
注意调度策略需要配置为非抢占式的内核,若是抢占式的,则测试程序会无效(因为其他内核进程可能会主动抢占死锁的进程)。
编写演示程序
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
static int __init rlock_init(void)
{
while(1);
return 0;
}
static void __exit rlock_exit(void)
{
return;
}
module_init(rlock_init);
module_exit(rlock_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
本程序非常的简单,编写一个模块程序并在模块初始化函数中执行while(1)循环即可, 以此来触发insmod进程在rlock_init()函数中陷入R状态死锁。
在树莓派中加载该模块后直接中断就”挂死“了,然后再约20s后内核打印如下:
root@apple:~# insmod rlock.ko
[ 60.254450] NMI watchdog: BUG: soft lockup - CPU#0 stuck for 23s! [insmod:515]
[ 60.261684] Modules linked in: rlock(O+) sg bcm2835_gpiomem bcm2835_wdt(O) uio_pdrv_genirq uio
[ 60.270344] CPU: 0 PID: 515 Comm: insmod Tainted: G O 4.1.15 #8
[ 60.277382] Hardware name: BCM2708
[ 60.280783] task: c591df60 ti: c5eaa000 task.ti: c5eaa000
[ 60.286189] PC is at rlock_init+0xc/0x10 [rlock]
[ 60.290812] LR is at do_one_initcall+0x90/0x1e8
[ 60.295342] pc : [<bf02e00c>] lr : [<c0009558>] psr: 60000013
[ 60.295342] sp : c5eabdc8 ip : c5eabdd8 fp : c5eabdd4
[ 60.306803] r10: 00000000 r9 : 00000124 r8 : bf02e000
[ 60.312020] r7 : bf02c0a4 r6 : c5eed660 r5 : c0bbd6e8 r4 : c0bbd6e8
[ 60.318539] r3 : 00000000 r2 : c6c01f00 r1 : 60000013 r0 : 60000013
[ 60.325058] Flags: nZCv IRQs on FIQs on Mode SVC_32 ISA ARM Segment user
[ 60.332183] Control: 00c5387d Table: 05828008 DAC: 00000015
[ 60.337924] CPU: 0 PID: 515 Comm: insmod Tainted: G O 4.1.15 #8
[ 60.344958] Hardware name: BCM2708
[ 60.348410] [<c0016660>] (unwind_backtrace) from [<c0013524>] (show_stack+0x20/0x24)
[ 60.356168] [<c0013524>] (show_stack) from [<c0526c54>] (dump_stack+0x20/0x28)
[ 60.363398] [<c0526c54>] (dump_stack) from [<c0010ae4>] (show_regs+0x1c/0x20)
[ 60.370547] [<c0010ae4>] (show_regs) from [<c0097444>] (watchdog_timer_fn+0x160/0x1a4)
[ 60.378482] [<c0097444>] (watchdog_timer_fn) from [<c006495c>] (__run_hrtimer+0x68/0x1c4)
[ 60.386668] [<c006495c>] (__run_hrtimer) from [<c00651b0>] (hrtimer_interrupt+0x104/0x270)
[ 60.394942] [<c00651b0>] (hrtimer_interrupt) from [<c001f394>] (bcm2708_timer_interrupt+0x38/0x48)
[ 60.403911] [<c001f394>] (bcm2708_timer_interrupt) from [<c0059e5c>] (handle_irq_event_percpu+0x5c/0x200)
[ 60.413481] [<c0059e5c>] (handle_irq_event_percpu) from [<c005a038>] (handle_irq_event+0x38/0x48)
[ 60.422359] [<c005a038>] (handle_irq_event) from [<c005ca64>] (handle_level_irq+0x98/0x114)
[ 60.430712] [<c005ca64>] (handle_level_irq) from [<c0059760>] (__handle_domain_irq+0x7c/0xdc)
[ 60.439244] [<c0059760>] (__handle_domain_irq) from [<c00107b4>] (handle_IRQ+0x2c/0x30)
[ 60.447251] [<c00107b4>] (handle_IRQ) from [<c0009340>] (asm_do_IRQ+0x18/0x1c)
[ 60.454485] [<c0009340>] (asm_do_IRQ) from [<c052b738>] (__irq_svc+0x38/0xb0)
[ 60.461613] Exception stack(0xc5eabd80 to 0xc5eabdc8)
[ 60.466670] bd80: 60000013 60000013 c6c01f00 00000000 c0bbd6e8 c0bbd6e8 c5eed660 bf02c0a4
[ 60.474845] bda0: bf02e000 00000124 00000000 c5eabdd4 c5eabdd8 c5eabdc8 c0009558 bf02e00c
[ 60.483010] bdc0: 60000013 ffffffff
[ 60.486515] [<c052b738>] (__irq_svc) from [<bf02e00c>] (rlock_init+0xc/0x10 [rlock])
[ 60.494271] [<bf02e00c>] (rlock_init [rlock]) from [<c0009558>] (do_one_initcall+0x90/0x1e8)
[ 60.502721] [<c0009558>] (do_one_initcall) from [<c007ad04>] (do_init_module+0x6c/0x1c0)
[ 60.510819] [<c007ad04>] (do_init_module) from [<c007c620>] (load_module+0x1690/0x1d34)
[ 60.518827] [<c007c620>] (load_module) from [<c007cda0>] (SyS_init_module+0xdc/0x130)
[ 60.526662] [<c007cda0>] (SyS_init_module) from [<c000f800>] (ret_fast_syscall+0x0/0x54)
[ 60.534745] Kernel panic - not syncing: softlockup: hung tasks
[ 60.540577] CPU: 0 PID: 515 Comm: insmod Tainted: G O L 4.1.15 #8
[ 60.547613] Hardware name: BCM2708
[ 60.551033] [<c0016660>] (unwind_backtrace) from [<c0013524>] (show_stack+0x20/0x24)
[ 60.558781] [<c0013524>] (show_stack) from [<c0526c54>] (dump_stack+0x20/0x28)
[ 60.566005] [<c0526c54>] (dump_stack) from [<c0523958>] (panic+0x90/0x1fc)
[ 60.572885] [<c0523958>] (panic) from [<c009746c>] (watchdog_timer_fn+0x188/0x1a4)
[ 60.580464] [<c009746c>] (watchdog_timer_fn) from [<c006495c>] (__run_hrtimer+0x68/0x1c4)
[ 60.588648] [<c006495c>] (__run_hrtimer) from [<c00651b0>] (hrtimer_interrupt+0x104/0x270)
[ 60.596917] [<c00651b0>] (hrtimer_interrupt) from [<c001f394>] (bcm2708_timer_interrupt+0x38/0x48)
[ 60.605881] [<c001f394>] (bcm2708_timer_interrupt) from [<c0059e5c>] (handle_irq_event_percpu+0x5c/0x200)
[ 60.615450] [<c0059e5c>] (handle_irq_event_percpu) from [<c005a038>] (handle_irq_event+0x38/0x48)
[ 60.624326] [<c005a038>] (handle_irq_event) from [<c005ca64>] (handle_level_irq+0x98/0x114)
[ 60.632680] [<c005ca64>] (handle_level_irq) from [<c0059760>] (__handle_domain_irq+0x7c/0xdc)
[ 60.641211] [<c0059760>] (__handle_domain_irq) from [<c00107b4>] (handle_IRQ+0x2c/0x30)
[ 60.649218] [<c00107b4>] (handle_IRQ) from [<c0009340>] (asm_do_IRQ+0x18/0x1c)
[ 60.656450] [<c0009340>] (asm_do_IRQ) from [<c052b738>] (__irq_svc+0x38/0xb0)
[ 60.663578] Exception stack(0xc5eabd80 to 0xc5eabdc8)
[ 60.668633] bd80: 60000013 60000013 c6c01f00 00000000 c0bbd6e8 c0bbd6e8 c5eed660 bf02c0a4
[ 60.676806] bda0: bf02e000 00000124 00000000 c5eabdd4 c5eabdd8 c5eabdc8 c0009558 bf02e00c
[ 60.684972] bdc0: 60000013 ffffffff
[ 60.688477] [<c052b738>] (__irq_svc) from [<bf02e00c>] (rlock_init+0xc/0x10 [rlock])
[ 60.696227] [<bf02e00c>] (rlock_init [rlock]) from [<c0009558>] (do_one_initcall+0x90/0x1e8)
[ 60.704671] [<c0009558>] (do_one_initcall) from [<c007ad04>] (do_init_module+0x6c/0x1c0)
[ 60.712765] [<c007ad04>] (do_init_module) from [<c007c620>] (load_module+0x1690/0x1d34)
[ 60.720771] [<c007c620>] (load_module) from [<c007cda0>] (SyS_init_module+0xdc/0x130)
[ 60.728607] [<c007cda0>] (SyS_init_module) from [<c000f800>] (ret_fast_syscall+0x0/0x54)
PANIC: softlockup: hung tasks
三、总结
R状态死锁是在进程上下文或中断上下文中出现的一种长期占用cpu的非正常现象, 在不易复现的环境中比较难以定位。本文分析了内核提供的监测其中在进程上下文中死锁的SOFTLOCKUP_DETECTOR 机制原理及实现方式。开发人员可通过这种机制较为有效的定位问题。
文档信息
--------------
* 版权声明:自由转载-非商用
* 转载: [My Linux Journey]