TKIP加密过程
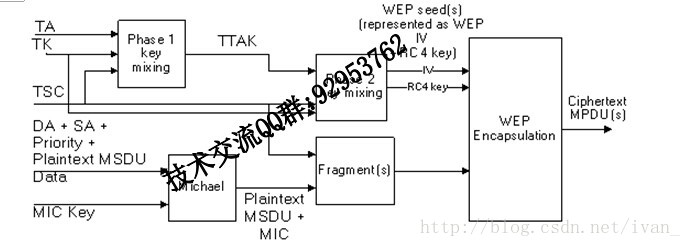
TA: 发送端MAC地址
TK: 握手中生产的TK
TSC: 发送端维护的序列号计数器
本想翻译下的,但是怕有误,还是直接上e文吧,原汁原味:
TKIP enhances the WEP encapsulation with several additional functions, as depicted in Figure 43c.
- TKIP MIC computation protects the MSDU Data field and corresponding SA, DA, and Priority fields. The computation of the MIC is performed on the ordered concatenation of the SA, DA, Priority, and MSDU Data fields. The MIC is appended to the MSDU Data field. TKIP discards any MIC padding prior to appending the MIC.
- If needed, IEEE 802.11 fragments the MSDU with MIC into one or more MPDUs. TKIP assigns a monotonically increasing TSC value to each MPDU, taking care that all the MPDUs generated from the same MSDU have the same value of extended IV (see 8.3.2.2).
- For each MPDU, TKIP uses the key mixing function to compute the WEP seed.
- TKIP represents the WEP seed as a WEP IV and RC4 key and passes these with each MPDU to WEP for generation of the ICV (see 7.1.3.6), and for encryption of the plaintext MPDU, including all or part of the MIC, if present. WEP uses the WEP seed as a WEP default key, identified by a key identifier associated with the temporal key.
NOTE—When the TSC space is exhausted, the choices available to an implementation are to replace the temporal key with a new one or to end communications. Reuse of any TSC value compromises already sent traffic.
Note that retransmitted MPDUs reuse the TSC without any compromise of security. The TSC is large enough,however, that TSC space exhaustion should not be an issue.
In Figure 43c, the TKIP-mixed transmit address and key (TTAK) denotes the intermediate key produced by Phase 1 of the TKIP mixing function (see 8.3.2.5).
TKIP解密过程:
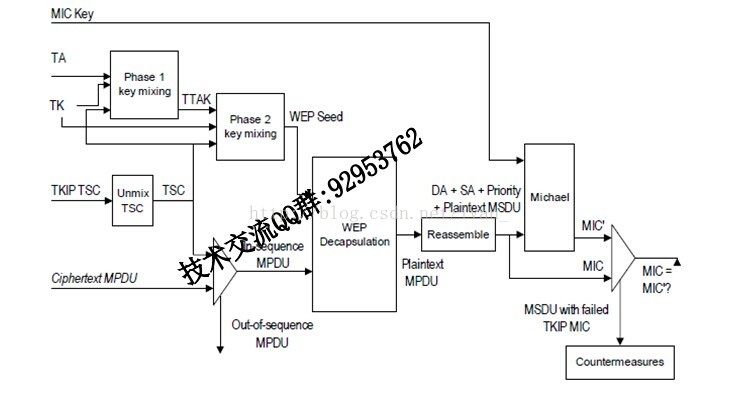
MIC Key:由握手生成
TA:发送端MAC地址
TK:握手中生成的TK
TSC:发送端维护的序列号计数器
Ciphertext MPDU:密文内容
解密过程:
TKIP enhances the WEP decapsulation process with the following additional steps:
a) Before WEP decapsulates a received MPDU, TKIP extracts the TSC sequence number and key
identifier from the WEP IV and the extended IV. TKIP discards a received MPDU that violates the
sequencing rules (see 8.3.2.6) and otherwise uses the mixing function to construct the WEP seed.
b) TKIP represents the WEP seed as a WEP IV and RC4 key and passes these with the MPDU to WEP
for decapsulation.
c) If WEP indicates the ICV check succeeded, the implementation reassembles the MPDU into an
MSDU. If the MSDU defragmentation succeeds, the receiver verifies the TKIP MIC. If MSDU
defragmentation fails, then the MSDU is discarded.
d) The MIC verification step recomputes the MIC over the MSDU SA, DA, Priority, and MSDU Data
fields (but not the TKIP MIC field). The calculated TKIP MIC result is then compared bit-wise
against the received MIC.
e) If the received and the locally computed MIC values are identical, the verification succeeds, and
TKIP shall deliver the MSDU to the upper layer. If the two differ, then the verification fails; the
receiver shall discard the MSDU and shall engage in appropriate countermeasures.
TKIP数据帧格式:
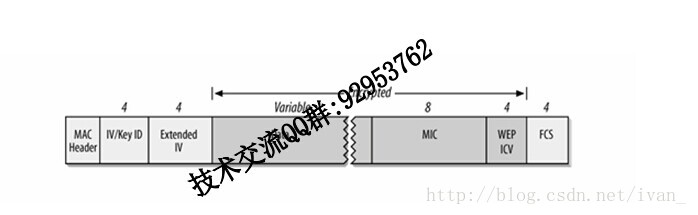
IV:初始化向量
Key ID:TKIP 的Key ID固定为零。
EIV:发送端维护的系列计数器的后16位;
MIC:发送端的MIC
WPA-PSK,WPA2-PSK加密过程
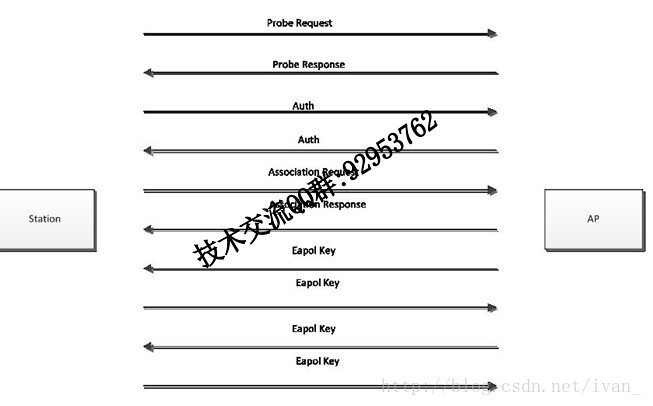
- Station发出一个Proble Request广播,寻找周围的AP
- AP收到Proble Request广播后回复Proble Response
- Station发出一个Auth,声明Auth Algorithm是Open System;
- AP收到Station发出一个Auth后,回复一个Auth,认可Auth Algorithm是Open System,置Status Code为0
- Station发出一个Association Request,请求是否匹配相关参数
- AP收到Association Request后,会仔细核查基本速率等参数;匹配的话回复一个Association Response。
- AP与Station 进行WPA-4HANDSHAKE,完成单播和组播/广播的密钥的生成。(重头戏)
WPA-4HANDSHAKE:
WPA-4HANDSHAKE是基于802.1X 协议,使用eapol key进行封装传输。
单播密钥
AP初始化:
使用 SSID 和passphares作为入参,通过哈希算法产生PSK。在WPA-PSK 中PMK=PSK。
第一次握手:
AP广播SSID,AP_MAC;
STATION 端使用接受到的SSID,AP_MAC和passphares使用同样算法产生PSK
第二次握手
STATION 发送一个随机数SNonce,STATION_MAC(SA)给AP;
AP端接受到SNonce,STATION_MAC(SA)后产生一个随机数ANonce,然后用PMK,AP_MAC(AA),STATION_MAC(SA),SNonce,ANonce 用以下SHA1_PRF算法产生PTK,提取这个PTK 前16 个字节组成一个MIC KEY。
第三次握手:
AP发送上面产生的ANonce给STATION
STATION 端用接收到ANonce 和以前产生PMK,SNonce,AP_MAC(AA),STATION_MAC(SA)用同样的算法产生PTK。 提取这个PTK 前16 个字节组成一个MIC KEY使用以下算法产生MIC值用这个MIC KEY 和一个802.1X数据帧使用以下算法得到MIC值
MIC = HMAC_MD5(MIC Key,16,802.1X data)
第四次握手:
STATION 发送802.1X 数据帧,MIC给AP;STATION 端用上面那个准备好的802.1X 数据帧在最后填充上MIC值和两个字节的0(十六进制)然后发送这个数据帧到AP。
AP端收到这个数据帧后提取这个MIC。并把这个数据帧的MIC部分都填上0(十六进制) 这时用这个802.1X数据帧,和用上面AP产生的MIC KEY 使用同样的算法得出MIC’。如果MIC’等于STATION 发送过来的MIC。 那么第四次握手成功。若不等说明则AP 和STATION 的密钥不相同,握手失败了。
通过四次握手和经过相关算法得到以下密钥,用于加密不同的数据类型
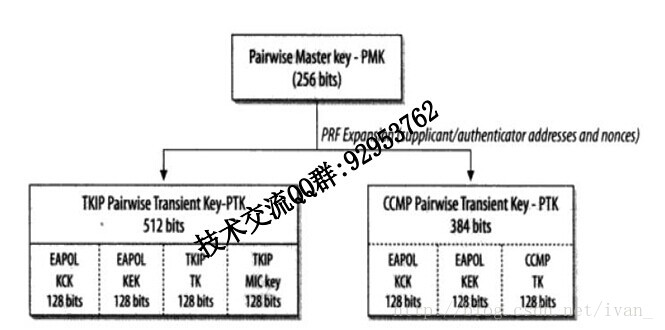
EAPOL KCK(key confirmation key):密钥确认密钥,用来计算密钥生成消息的完整性
EAPOL KEK(key Encryption key):密钥加密密钥,用来加密密钥生成消息
TKIP TK(CCMP TK):这部分用来对单播数据的加密
TKIP MIC key:用于Michael完整性校验的(只有TKIP有)
组播密钥
GMK主组密钥(group master key)以作为临时密钥的基础 和成对密钥一样扩展获得GTK (groupTransient Key) 公式如下: GTK=PRF-X(GMK,”Group key expansion”,AA||GN) GN - AP 生成的 Nonce AA - AP MAC地址
GMK(Group Master Key,组主密钥):认证者用来生成组临时密钥(GTK)的密钥,通常是认证者生成的一组随机数。
GTK(Group Transient Key,组临时密钥):由组主密钥(GMK)通过哈希运算生成,是用来保护广播和组播数据的密钥。
文档信息
--------------
* 作者:
* 版权声明:自由转载-非商用
* 转载: []聚焦物联网 wifi技术交流群QQ:92953762